How Car Accidents Cause Brain Injuries
Car accidents range in severity from a simple fender-bender to a more dangerous rollover accident. People may be quick to assume that, in a crash that did not even cause much of a dent, no serious injuries can occur. However, one should never make this assumption. For example, an individual can sustain whiplash from another car crashing into theirs from behind. A serious complication from this involves brain injuries, which one might not expect to suffer from a fender-bender. Nevertheless, anything is possible, and brain injuries must be treated quickly and carefully.
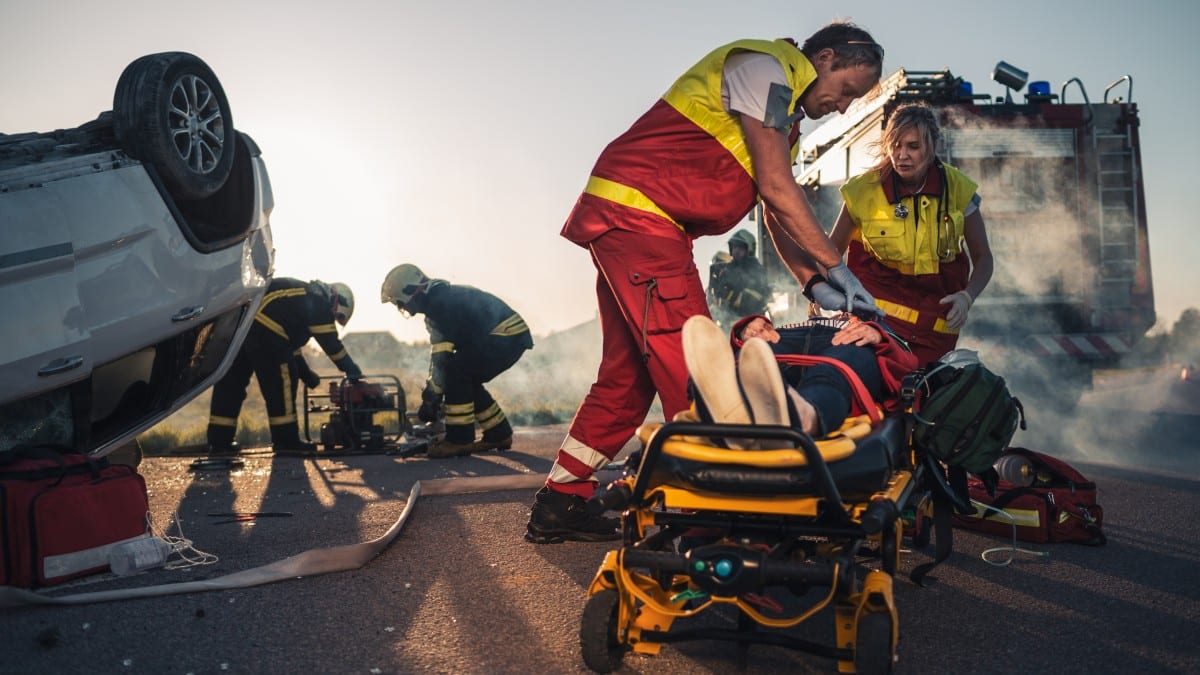

What is an acquired brain injury?
Acquired brain injuries (ABIs) are not hereditary and do not occur before birth. There is a change in the brain’s neuronal activity, affecting all other systems in the body. At times, the injured person may appear to be perfectly fine, but delayed trauma can ensue. Swelling starts to happen, which blocks off the oxygen supply to the brain. From there, many other parts of the body are affected, such as your circulatory system and your other organs. If medical treatment is not provided right away, a brain injury could be fatal.
What types of brain injuries are there?
There are two types of acquired brain injuries: non-traumatic and traumatic. Non-traumatic brain injuries are those that occur without a physical cause, such as stroke, encephalitis, and seizures. Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) occur when there is a sudden impact to the head. It could be a hard blow to the head or could involve a sharp item penetrating the brain. These are caused by assault, falls, sports, and of course, car accidents.
There are a few main types of TBIs that result from car accidents.
- Concussions are the mildest form of TBI, causing speech and memory issues. Although the person seems fine and may not feel the need to see a medical professional, leaving this problem unchecked could lead to long-term damage.
- A hematoma occurs when the body starts to react to the blow by clotting to reduce blood flow. If large enough, some hematomas can only be surgically removed. Not treating a hematoma can also cause many other issues, like a series of strokes.
- A contusion, or brain bruising, can also happen because of a car accident. The brain tissue, veins, and arteries become swollen, and blood vessels could begin to leak. Tumors can develop and become life-threatening. A diffuse axonal injury (DAI) happens when the brain moves aggressively back and forth in the skull. The nerve axons within the brain can begin to tear, and the individual is typically left in a coma. It is one of the most common types of TBIs, and unfortunately, one of the most destructive, as well. Ironically, the changes in the brain are so small that they can be challenging to detect in an imaging scan.
- Another type is a traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage (TSAH), which takes place when the cerebrospinal fluid cushion that normally fills the space around the brain is impacted and torn, leading to bleeding, brain inflammation, and brain cell damage.
Types of accidents that can cause brain injuries
Just as many types of car accidents can happen, several types of traumatic brain injuries can occur in any of them. If an individual is sitting at a red light, and the car behind them suddenly crashes into the back of their car, the driver’s head can propel forward at high speeds – straight into the steering wheel. A situation like this leads to what is called a coup contrecoup injury: when the injury occurs at both the site of trauma and the opposite side of it. In other words, when the individual hits the steering wheel, the front part of their brain is the first part to take the hit. However, through momentum and because the brain has a pudding-like consistency, the movement of the brain causes another impact against the back of the head.
These types of brain injuries can also happen when a larger vehicle crashes into either side of the victim’s car. Assume a commercial truck runs a red light and does not see the car that is about to proceed. This truck, being so many times heavier than the car, hits the driver’s side head-on. The car driver’s head involuntarily moves from side to side because of the force, leading to a TBI. The driver’s head can also collide with the window, giving way to more risk for a TBI.
Rollover accidents might just be one of the most serious ones regarding the risk of sustaining a TBI. Here, the brain can be subjected to hard blows, penetrating injuries, and severe pressure. There are higher chances of skull fractures with these types of accidents due to their nature. Since impact velocity, angle, and momentum all affect the severity of a TBI, it may not make much of a difference if the vehicle rolled over once, twice, or more. Just one turn can send the injured victim to the hospital with a life-threatening TBI.
What should you do if you suspect a brain injury?
It’s important to remember that even if you cannot see an injury, it does not mean that it is not there. TBIs can lead to several long-term complications, like memory loss, lack of emotional control, inability to communicate, and so much more. After a car accident, even if it seems like you came out okay, it’s important to find yourself a medical professional right away so that they can assess you. Be sure to keep all the medical bills and doctors’ notes so that they can be used as proper documentation in the case later.
Car accidents can lead to life-changing events, like traumatic brain injuries, that will leave the injured party with expenses that can last a lifetime. If you or a loved one experienced a brain injury due to a car accident, get in touch with an experienced lawyer right away from Kansas City Accident Injury Attorneys. Contact our Kansas City, MO, office today to schedule a free, no-obligation consultation.
We also have locations in Lee’s Summit, Parkville, and St. Joseph, Missouri. We have offices located in Kansas in Olathe, Kansas City, and Overland Park. These locations are by appointment only.
Related Content:

Kansas City personal injury attorney James Roswold of Kansas City Accident Injury Attorneys handles cases dealing with victims of personal injury, medical negligence, wrongful death, workers compensation, nursing home negligence, premises liability, product liability, car accident, truck accident and motorcycle accident cases.